自组织映射网络 -用python实现SOM(用于聚类)
分类: Java 标签: python som 自组织映射网络
2021-01-14 22:47:00 1530浏览
自组织映射网络 -用python实现SOM(用于聚类)
主题:自组织映射网络 -用python实现SOM(用于聚类)
前言:
SOM(Self Organizing Maps ) 得目标是用低维目标空间得点来表示高维空间中得点,并且尽可能保持对应点得距离和邻近关系(拓扑关系)。该算法可用于降维和聚类等方面,本文通过python实现了该算法在聚类方面得应用,并将代码进行了封装,方便读者调用。
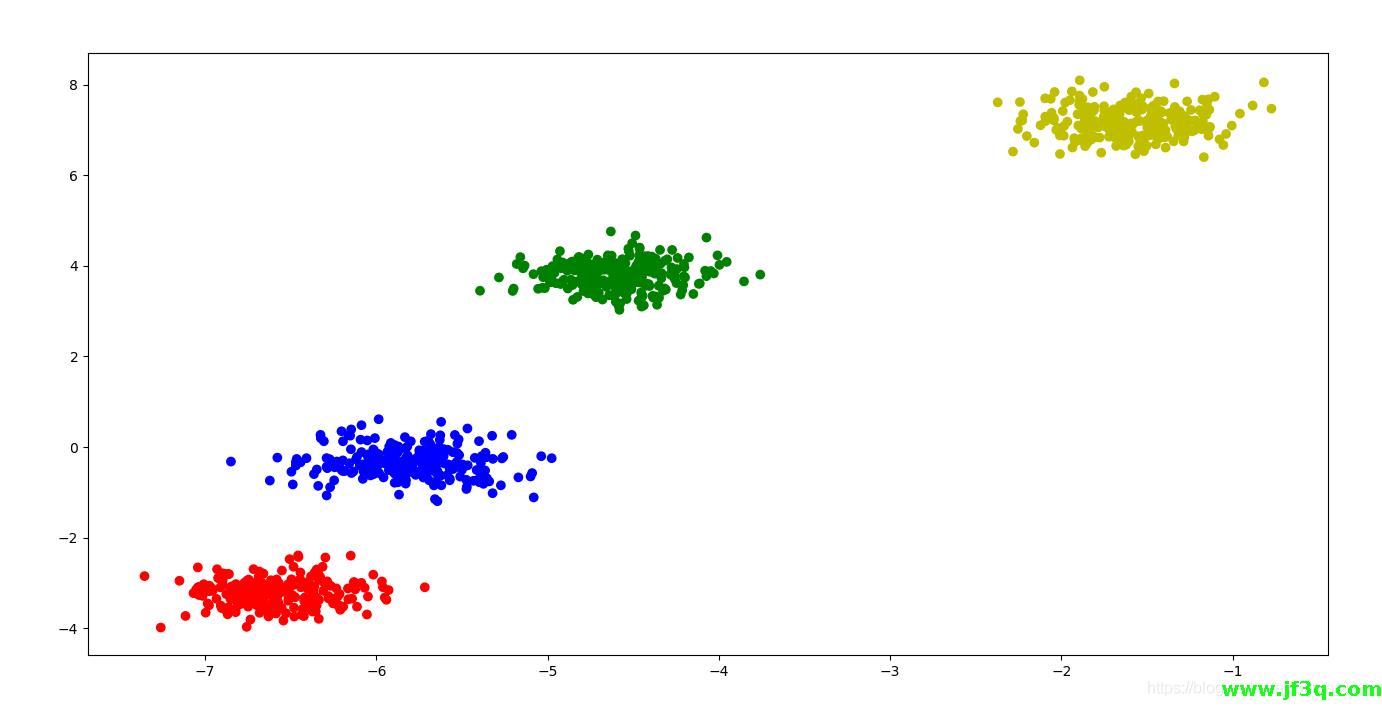
下图为正文计算实例得可视化图形。

python实现代码
net:竞争层得拓扑结构,支持一维及二维,1表示该输出节点存在,0表示不存在该输出节点
epochs:最大迭代次数
.r_t:[C,B] 领域半径参数,r = C*e**(-B * t/eoochs),其中t表示当前迭代次数
eps:[C,B] learning rate得阈值
用法:指定竞争层得拓扑结构、 最大迭代次数、领域半径参数、学习率阈值(后三个参数也可不指定),竞争层得拓扑结构得节点数代表了聚类数目,然后直接调用fit(X) 进行数据集得聚类。
对簇形状数据集进行聚类
仅需五步即可实现较好得聚类结果
行,今天就给大家分享到这里吧,您的一份支持就是我最大的动力,最后打个小广告,我们程序员在学习和工作中或多或少会遇到一些比较棘手的问题,也就所谓的一时半会解决不了的bug,可以来杰凡IT问答平台上提问,平台上大佬很多可以快速给你一对一解决问题,有需要的朋友可以去关注下,平台网址: https://www.jf3q.com
前言:
SOM(Self Organizing Maps ) 得目标是用低维目标空间得点来表示高维空间中得点,并且尽可能保持对应点得距离和邻近关系(拓扑关系)。该算法可用于降维和聚类等方面,本文通过python实现了该算法在聚类方面得应用,并将代码进行了封装,方便读者调用。
下图为正文计算实例得可视化图形。

python实现代码
net:竞争层得拓扑结构,支持一维及二维,1表示该输出节点存在,0表示不存在该输出节点
epochs:最大迭代次数
.r_t:[C,B] 领域半径参数,r = C*e**(-B * t/eoochs),其中t表示当前迭代次数
eps:[C,B] learning rate得阈值
用法:指定竞争层得拓扑结构、 最大迭代次数、领域半径参数、学习率阈值(后三个参数也可不指定),竞争层得拓扑结构得节点数代表了聚类数目,然后直接调用fit(X) 进行数据集得聚类。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-计算实例
# @Time : 2021/1/12 22:37
# @Author : CyrusMay WJ
# @FileName: SOM.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# @Blog :https://blog.csdn.net/Cyrus_May
import numpy as np
import random
np.random.seed(22)
class CyrusSOM(object):
def __init__(self,net=[[1,1],[1,1]],epochs = 50,r_t = [None,None],eps=1e-6):
"""
:param net: 竞争层得拓扑结构,支持一维及二维,1表示该输出节点存在,0表示不存在该输出节点
:param epochs: 最大迭代次数
:param r_t: [C,B] 领域半径参数,r = C*e**(-B*t/eoochs),其中t表示当前迭代次数
:param eps: learning rate得阈值
"""
self.epochs = epochs
self.C = r_t[0]
self.B = r_t[1]
self.eps = eps
self.output_net = np.array(net)
if len(self.output_net.shape) == 1:
self.output_net = self.output_net.reshape([-1,1])
self.coord = np.zeros([self.output_net.shape[0],self.output_net.shape[1],2])
for i in range(self.output_net.shape[0]):
for j in range(self.output_net.shape[1]):
self.coord[i,j] = [i,j]
print(self.coord)
def __r_t(self,t):
if not self.C:
return 0.5
else:
return self.C*np.exp(-self.B*t/self.epochs)
def __lr(self,t,distance):
return (self.epochs-t)/self.epochs*np.exp(-distance)
def standard_x(self,x):
x = np.array(x)
for i in range(x.shape[0]):
x[i,:] = [value/(((x[i,:])**2).sum()**0.5) for value in x[i,:]]
return x
def standard_w(self,w):
for i in range(w.shape[0]):
for j in range(w.shape[1]):
w[i,j,:] = [value/(((w[i,j,:])**2).sum()**0.5) for value in w[i,j,:]]
return w
def cal_similar(self,x,w):
similar = (x*w).sum(axis=2)
coord = np.where(similar==similar.max())
return [coord[0][0],coord[1][0]]
def update_w(self,center_coord,x,step):
for i in range(self.coord.shape[0]):
for j in range(self.coord.shape[1]):
distance = (((center_coord-self.coord[i,j])**2).sum())**0.5
if distance <= self.__r_t(step):
self.W[i,j] = self.W[i,j] + self.__lr(step,distance)*(x-self.W[i,j])
def transform_fit(self,x):
self.train_x = self.standard_x(x)
self.W = np.zeros([self.output_net.shape[0],self.output_net.shape[1],self.train_x.shape[1]])
for i in range(self.W.shape[0]):
for j in range(self.W.shape[1]):
self.W[i,j,:] = self.train_x[random.choice(range(self.train_x.shape[0])),:]
self.W = self.standard_w(self.W)
for step in range(int(self.epochs)):
j = 0
if self.__lr(step,0) <= self.eps:
break
for index in range(self.train_x.shape[0]):
print("*"*8,"({},{})/{} W:\n".format(step,j,self.epochs),self.W)
center_coord = self.cal_similar(self.train_x[index,:],self.W)
self.update_w(center_coord,self.train_x[index,:],step)
self.W = self.standard_w(self.W)
j += 1
label = []
for index in range(self.train_x.shape[0]):
center_coord = self.cal_similar(self.train_x[index, :], self.W)
label.append(center_coord[1]*self.coord.shape[1] + center_coord[0])
class_dict = {}
for index in range(self.train_x.shape[0]):
if label[index] in class_dict.keys():
class_dict[label[index]].append(index)
else:
class_dict[label[index]] = [index]
cluster_center = {}
for key,value in class_dict.items():
cluster_center[key] = np.array([x[i, :] for i in value]).mean(axis=0)
self.cluster_center = cluster_center
return label
def fit(self,x):
self.train_x = self.standard_x(x)
self.W = np.random.rand(self.output_net.shape[0], self.output_net.shape[1], self.train_x.shape[1])
self.W = self.standard_w(self.W)
for step in range(int(self.epochs)):
j = 0
if self.__lr(step,0) <= self.eps:
break
for index in range(self.train_x.shape[0]):
print("*"*8,"({},{})/{} W:\n".format(step, j, self.epochs), self.W)
center_coord = self.cal_similar(self.train_x[index, :], self.W)
self.update_w(center_coord, self.train_x[index, :], step)
self.W = self.standard_w(self.W)
j += 1
label = []
for index in range(self.train_x.shape[0]):
center_coord = self.cal_similar(self.train_x[index, :], self.W)
label.append(center_coord[1] * self.coord.shape[1] + center_coord[1])
class_dict = {}
for index in range(self.train_x.shape[0]):
if label[index] in class_dict.keys():
class_dict[label[index]].append(index)
else:
class_dict[label[index]] = [index]
cluster_center = {}
for key, value in class_dict.items():
cluster_center[key] = np.array([x[i, :] for i in value]).mean(axis=0)
self.cluster_center = cluster_center
def predict(self,x):
self.pre_x = self.standard_x(x)
label = []
for index in range(self.pre_x.shape[0]):
center_coord = self.cal_similar(self.pre_x[index, :], self.W)
label.append(center_coord[1] * self.coord.shape[1] + center_coord[1])
return label
对簇形状数据集进行聚类
仅需五步即可实现较好得聚类结果
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris,make_blobs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
if __name__ == '__main__':
SOM = CyrusSOM(epochs=5)
data = make_blobs(n_samples=1000,n_features=2,centers=4,cluster_std=0.3)
x = data[0]
y_pre = SOM.transform_fit(x)
colors = "rgby"
figure = plt.figure(figsize=[20,12])
plt.scatter(x[:,0],x[:,1],c=[colors[i] for i in y_pre])
plt.show()
******** (4,998)/5 W:
[[[-0.90394221 -0.42765463]
[-0.99859415 -0.05300684]]
[[-0.77166042 0.63603475]
[-0.23064699 0.9730375 ]]]
******** (4,999)/5 W:
[[[-0.89968359 -0.4365426 ]
[-0.99859415 -0.05300684]]
[[-0.77166042 0.63603475]
[-0.23064699 0.9730375 ]]]

行,今天就给大家分享到这里吧,您的一份支持就是我最大的动力,最后打个小广告,我们程序员在学习和工作中或多或少会遇到一些比较棘手的问题,也就所谓的一时半会解决不了的bug,可以来杰凡IT问答平台上提问,平台上大佬很多可以快速给你一对一解决问题,有需要的朋友可以去关注下,平台网址: https://www.jf3q.com
好博客就要一起分享哦!分享海报
此处可发布评论
评论(0)展开评论
暂无评论,快来写一下吧
展开评论